Augmented Reality in Healthcare: Improving Patient Outcomes
Understanding Augmented Reality and Its Role in Healthcare
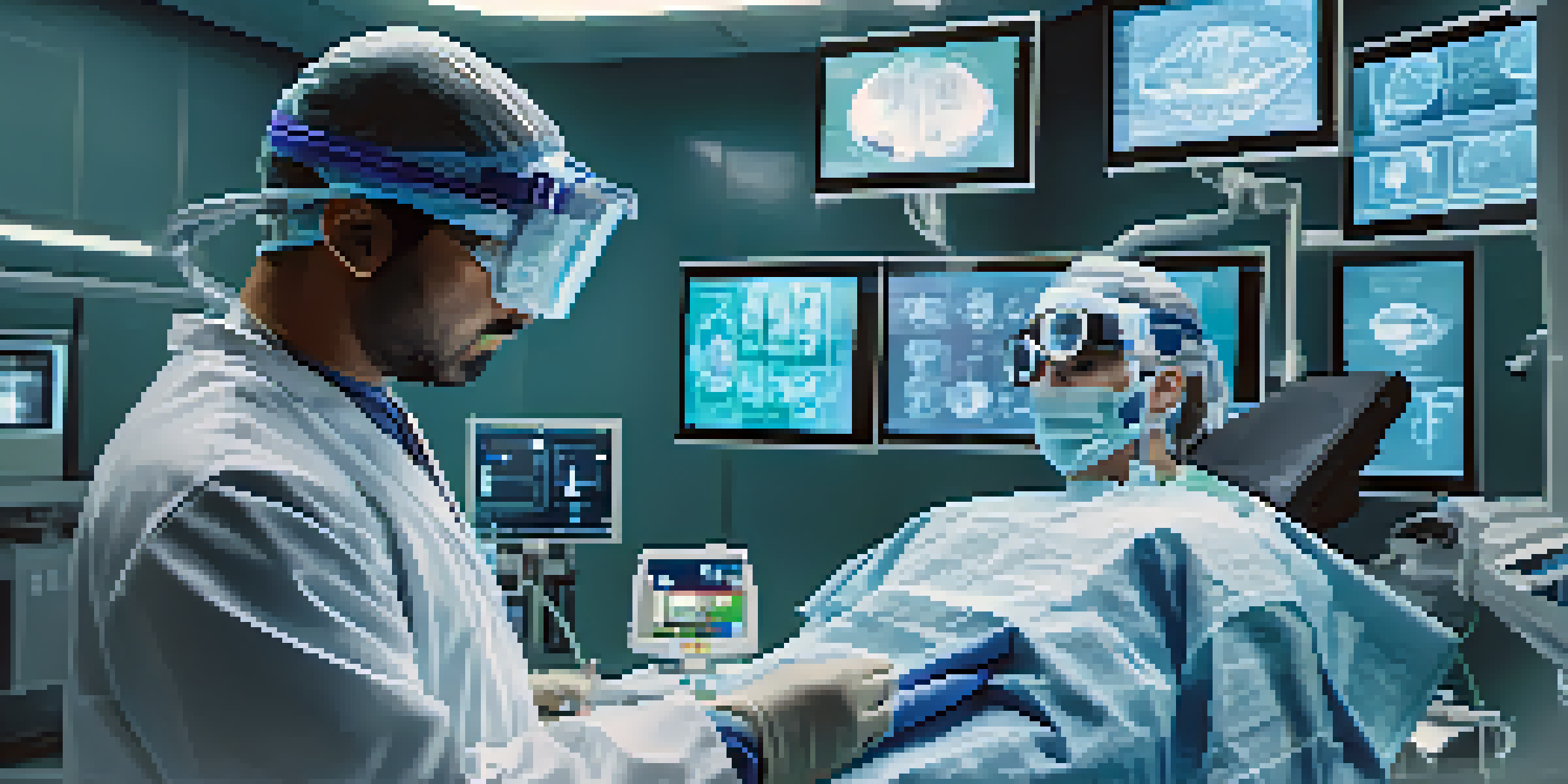
Augmented reality (AR) is an interactive experience that combines the real world with digital elements, enhancing our perception of reality. In healthcare, AR can visualize complex data, making it easier for medical professionals to understand and convey information. Imagine a surgeon wearing AR glasses that overlay critical patient data directly onto their field of vision during an operation—it can truly revolutionize surgical procedures.
Augmented reality is a revolutionary technology that has the potential to transform healthcare delivery, improve patient outcomes, and enhance medical training.
This technology is not just about flashy visuals; it's about practical applications that can improve patient outcomes. For instance, AR can help in training medical students, allowing them to practice procedures in a risk-free environment. By merging digital models with real-world scenarios, students can gain hands-on experience that traditional methods simply cannot provide.
Related Resource
As AR technology continues to advance, its applications in healthcare are expanding rapidly. From pre-operative planning to post-operative care, the potential for AR to enhance patient care is immense. It’s a glimpse into the future of medicine where technology and human skill work hand in hand.
Enhancing Surgical Precision with Augmented Reality
Surgical procedures often require remarkable precision, and augmented reality is stepping in to lend a helping hand. Surgeons can use AR to visualize internal anatomy during operations, significantly reducing the risk of errors. For example, AR can overlay a patient’s 3D imaging data onto their body, guiding surgeons through delicate procedures.

This technology not only enhances the accuracy of surgeries but also improves the overall efficiency of operations. By having critical information readily available in real-time, surgeons can make quicker decisions and reduce the duration of surgeries. This can lead to better recovery times for patients, which is a win-win for everyone involved.
AR Enhances Surgical Precision
Augmented reality allows surgeons to visualize internal anatomy, significantly reducing the risk of errors during complex procedures.
Moreover, AR can assist in complex procedures such as minimally invasive surgeries, where visibility is limited. By providing enhanced visual guidance, AR allows surgeons to navigate through intricate pathways with confidence. The result is a smoother surgical experience and, ultimately, better patient outcomes.
Improving Patient Education and Engagement through AR
Patient education plays a crucial role in healthcare, and augmented reality is making this process more engaging and effective. With AR, patients can visualize their medical conditions and treatment plans in a way that is easily digestible. Imagine a patient using an AR app that displays how a medication works within their body—this kind of interactive learning can empower patients to take charge of their health.
The integration of augmented reality in medical training can create a more immersive learning experience, better preparing healthcare professionals for real-world challenges.
Furthermore, AR can help in demystifying complex medical procedures, allowing patients to understand what to expect before they even step into the operating room. This transparency can reduce anxiety and build trust between patients and healthcare providers. When patients feel informed, they are more likely to adhere to treatment plans and participate actively in their care.
Related Resource
The potential for AR in patient education is vast, as it can cater to various learning styles. Whether someone prefers visual aids, interactive simulations, or step-by-step guides, AR can provide a tailored experience that resonates with individual needs. This personalized approach is key to enhancing patient engagement and improving overall health outcomes.
Transforming Physical Rehabilitation with Augmented Reality
Physical rehabilitation can be a challenging journey, but augmented reality is transforming how patients recover. By integrating AR into rehabilitation programs, patients can participate in engaging exercises that are both fun and effective. Imagine a patient using AR to play a game that encourages them to perform their prescribed movements—this gamification can make rehabilitation feel less like a chore.
Moreover, AR can provide real-time feedback on a patient’s movements, allowing them to correct their form and maximize the benefits of their exercises. This immediate guidance can lead to faster recovery times and improved outcomes. Patients are more likely to stay motivated when they see progress reflected in their performance.
AR Improves Patient Engagement
Through interactive visualizations, augmented reality empowers patients to better understand their health and treatment plans.
Additionally, AR can facilitate remote rehabilitation sessions, making it accessible for patients who may have difficulty attending in-person appointments. With AR, therapists can monitor progress from afar and adjust programs as needed. This flexibility ensures that patients continue their recovery journey, regardless of their circumstances.
Augmented Reality in Medical Training and Simulation
Training the next generation of healthcare professionals is a critical component of improving patient outcomes, and augmented reality is changing the game. Medical students can utilize AR to practice complex procedures in a safe environment, honing their skills before interacting with real patients. It’s like having a virtual mentor guiding them through each step, reducing the risks associated with traditional training methods.
Simulations powered by AR can replicate real-life scenarios, allowing students to experience the challenges they will face in the field. For instance, they can practice emergency responses in a controlled setting, preparing them for high-pressure situations. This hands-on experience fosters confidence and competence among future healthcare providers.
Related Resource
Furthermore, AR can facilitate collaborative learning, where multiple students can engage in a shared virtual environment. This team-based approach not only enhances communication skills but also mirrors the multidisciplinary nature of modern healthcare. By embracing AR in training, we are equipping healthcare professionals with the tools they need to deliver outstanding patient care.
Reducing Costs and Improving Efficiency in Healthcare Operations
One of the significant advantages of adopting augmented reality in healthcare is its potential to reduce costs while improving operational efficiency. By streamlining processes with AR technology, healthcare providers can minimize waste and optimize resource allocation. For example, AR can assist in inventory management by providing real-time data on supplies, ensuring that hospitals are well-stocked without over-purchasing.
Moreover, AR can enhance communication and collaboration among healthcare teams. With shared visualizations and data, team members can make informed decisions quickly, reducing delays in patient care. This efficiency can translate into shorter wait times and improved patient satisfaction, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
AR Transforms Medical Training
Augmented reality provides medical students with safe, hands-on practice opportunities, enhancing their skills before they work with real patients.
As healthcare systems grapple with rising costs, integrating AR technology can be a strategic move toward achieving financial sustainability. By investing in AR solutions, healthcare providers can not only enhance patient care but also ensure that resources are being used effectively. This dual benefit makes AR a compelling option for modern healthcare.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Augmented Reality in Healthcare
The future of augmented reality in healthcare is bright, with continued advancements promising even greater improvements in patient outcomes. As technology evolves, we can expect AR to become more integrated into daily medical practices. For instance, innovations in AR wearables could provide surgeons with hands-free access to crucial information during procedures, further enhancing precision and safety.
Additionally, the rise of telehealth has opened new avenues for AR applications. Remote consultations can be enriched with AR tools, allowing healthcare providers to visualize conditions and engage patients more effectively from a distance. This synergy between telehealth and AR could redefine how care is delivered, making it more accessible to patients worldwide.

Ultimately, as research continues and AR technology becomes more sophisticated, we will likely see a surge in its adoption across various healthcare settings. The potential benefits—improved patient outcomes, enhanced training, and increased efficiency—make AR a key player in the future of healthcare. Embracing this innovation could be the key to unlocking a new era of medical excellence.